Name: Capability Innovation Team
Based on: Organization or Project Team or Enabling System
There are various definitions of capabilities:
- ISO 9000:2015: ability of an object to realize an output that will fulfil the requirements for that output
- TOGAF 9.1: An ability that an organization, person, or system possesses. Capabilities are typically expressed in general and high-level terms and typically require a combination of organization, people, processes, and technology to achieve.
- DoDAF 2.0: The ability to achieve a Desired Effect under specified (performance) standards and conditions through combinations of ways and means (activities and resources) to perform a set of activities.
The Capability Innovation Team is also called:
-
Process Improvement Team or Process Team.
-
Quality Improvement Team, or Quality Team.
-
Business Improvement Team.
-
Capability Maturity Teams.
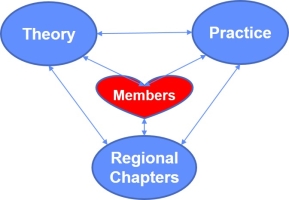
A Capability Innovation Team can also be seen as a Community of Practice (CoP). The model is shown below:
Practitioners using a capability are the members of the team and there are specialists that help define processes and tools / technology that are put into practice (tested) and then realized in organizations.
The Capability Innovation Team (CIT) is a type of enabling system for a capability. The purpose of this team is to establish and maintain a capability for use within organizations. The Capability Improvement Team is multi-disciplinary and enables the organization to:
-
Create or improve capabilities using a Project Management process supported by a Capability Innovation Life Cycle process
-
Monitor the performance of capabilities and look for opportunities to improve.
-
Take an integrated view of the capability to enable the best match / use of people and technology to achieve the outcomes and results of the process.
-
Ensure that capability realization is supported: collecting feedback, providing support for use, delivering coaching, etc.
-
Improve the maturity of the set of organizational capabilities
System Quantity Properties
-
Number of capabilities managed by the team
-
Size of the team
-
Number of teams using the capabilities managed by the team.
Systemic Measurable Variables
The performance of the Capability is identified and measured through the process system element: and include some or all of the following:
- Performance against Release Plan for the capability
- Ease of Use of the Process.
- Efficiency of the Technology supporting the Capability.
- Number of defects logged
- Time to resolve issues.
- Maturity of the capability
Systemic Capabilities or Functions
The capability is delivered according to the Capability Innovation Life Cycle process. The capability of this process is realized by the Capability Innovation Team..
System States
A Capability can be in various states as identified in the Capability Innovation Life Cycle:
- Architectural states
- Identified: The name of the capability is identified
- Defined: The capability description is complete. The definition is independent of the realization.
- Capability as defined in the capability description is planned..
- Transformational States
- Potential: A realized capability with versions of process, training and technology but not in use.
- Future: The desired state of the capability in the future (at a point in time).
- Release delivered according to Release Plan.
- Operational States
- Actual: An actual realized capability (people, process and technology) that is in use
- Current: The state of the capability today (at a point in time).
- Support Provided by the Capability Team
Capability Owners and Managers or Process Owners and Managers
- Do I have sufficient practitioner involvement in the creation and maintenance of the Capability?
- Do I have the tools and commitment to replicate the capability across the Organization?
- Is this Capability efficient and effective?
- Are changes and improvements to the Capability managed through practitioner feedback and delivered in a when needed?
- Is the capacity of the capability sufficient to achieve the organizational objectives?
- Is the plan using the Project Management fully funded and resourced?
Person (also called a practitioner or capability practitioner) taking on the roles and carrying out the work:
- Do I have the skills knowledge and experience to carry out the work?
- Are the activities easy to understand and carry out?
- Is the technology fit for purpose?
Team Manager
- Will this capability help us meet our objectives and purpose?
- How do I improve this capability?
Organizational Managers
-
Will this capability enable our enterprise to deliver to our customers?
-
Will this capability deliver benefits to our organization?
A Capability Team works with:
-
managers who are realizing the capability in their organization.
-
practitioners who will be developing skills, knowledge and experience using the process.
-
The managers that provide funding for the team to understand the benefits of the investments.
-
Human Resources staff to ensure that a competency framework, role / job descriptions, training, assessment are available
-
Information Technology staff to ensure that the technology items needed to perform the process are available and fit for purpose. These may also be involved if some new or revised requirements are needed in the technology.
System Element: Identification
The following picture highlights the structure of a capability improvement team. This team is typically formed as a project team formed using the Project Management
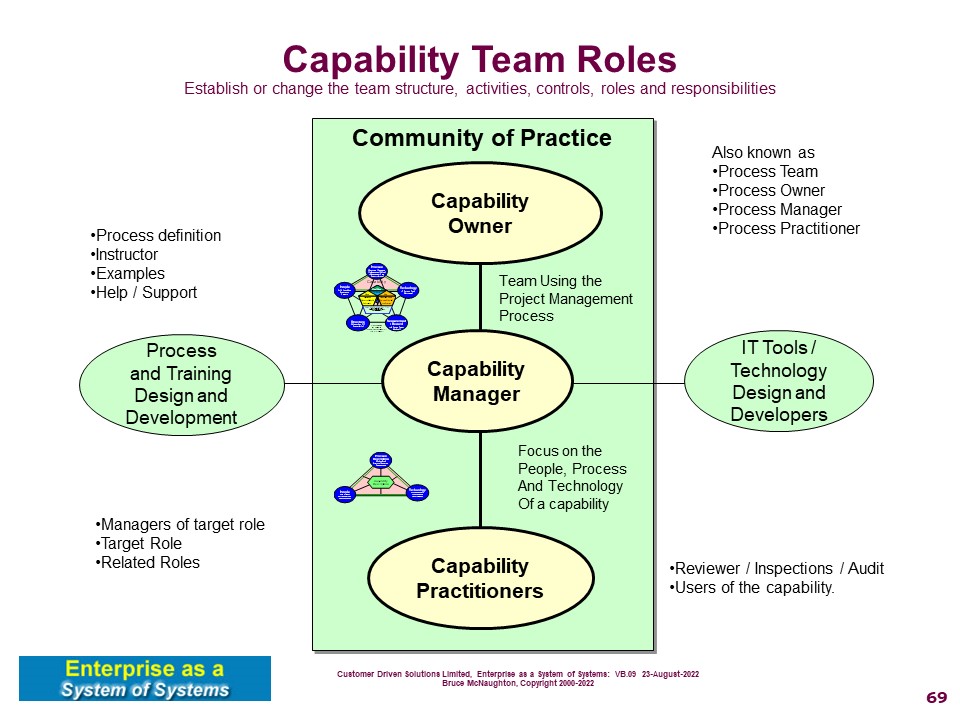
The Process documentation forms the key element of the teams responsibility
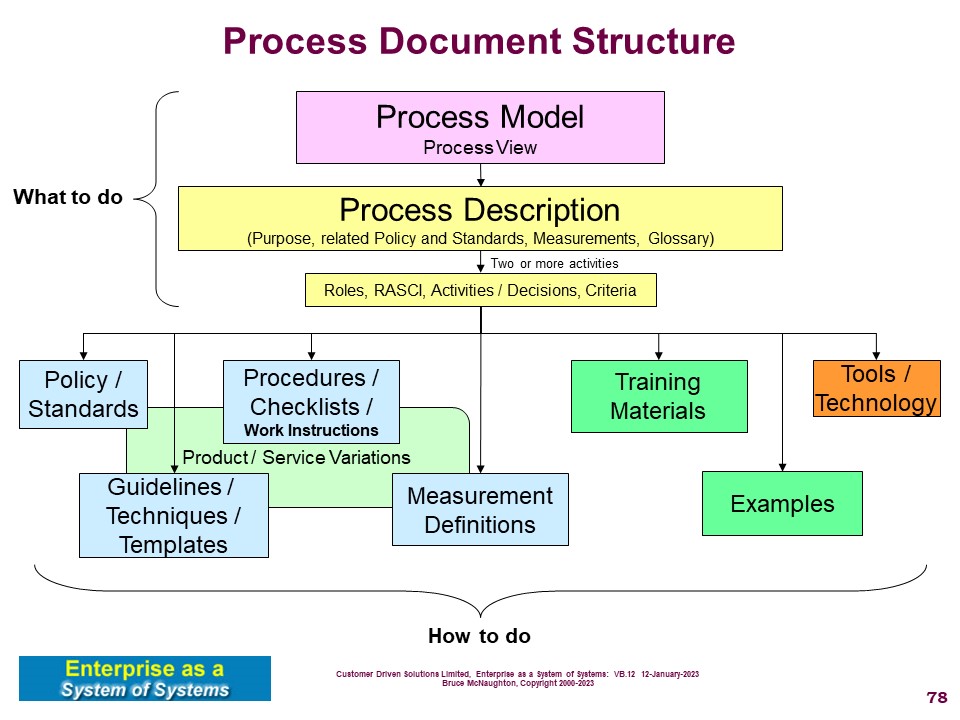
Configuration / Scenario:
Describes any configuration / scenario attributes for a specific system-of-interest. This may not be appropriate for all system descriptions (e.g. patterns or abstract systems).
Cyclical (Repeating / Regular) Processes
The Capability Innovation Team carries out the typical cyclical processes:
Trigger: Capability Review Complete; Process Revise plan based upon Capability Review.
Trigger: Log Issues; Process: Prioritise issues and handle appropriately
Trigger: Ready for Release of Capability; Process: Support the deployment of revised / new capability
Development Life Cycle Processes
The Capability Innovation Life Cycle identifies the key activities to create a Capability that can be replicated and implemented within a team or organization. The process activities are shown below:
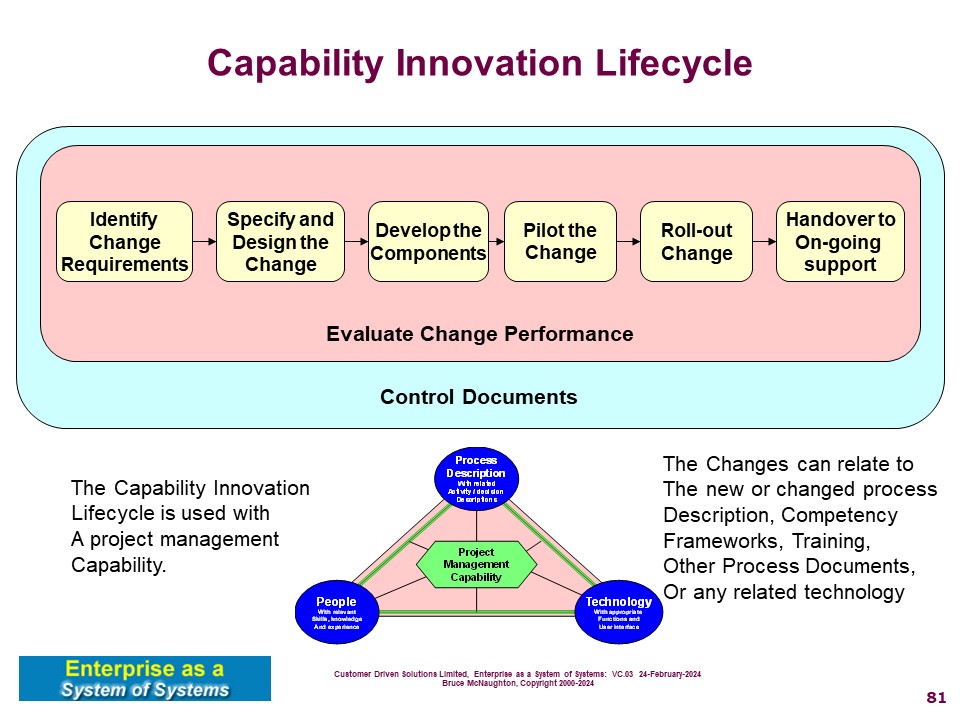
This work is generally carried out by a Capability Innovation Team using a project management process. (NOTE: In some places this may be called a Capability Improvement Team or other names). This capability team supports all of the teams or organizations using the Capability and uses the Capability Innovation Life Cycle
The definition of a capability involves the identification of the emergent properties needed within the organization. This can be defined in the architecture description or the design and implementation activities following the architecture. The underlying process and information form the basis for the capability realization. See the process design patterns for typical types of activities that support the means to realize a capability.
A process is a description of work to be performed within the context of an organization. The following picture provides a context for a process and capability within an organization.
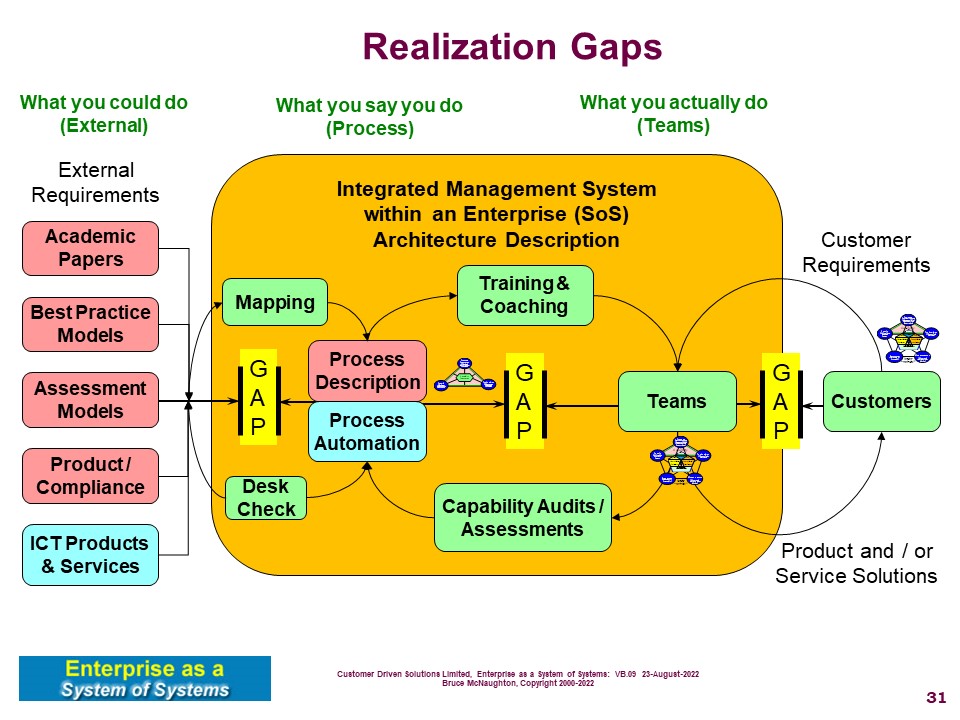
This diagram shows the process to bring external standards into an enterprise. Three gaps are managed in this process. All of these are addressed by this Capability Innovation Team using the Project Management and a Capability Innovation Life Cycle
The following references support this type of system-of-interest.