System: Technology System
Name: Technology System
Based on: Designed Physical System.
Abstract System: This system has been identified as an abstract system that cannot be implemented directly. The abstract system establishes a shared pattern of characteristics that any system can use to describe its unique characteristics when referenced in the 'based on' list above. These references are described using a generalization association in UML.
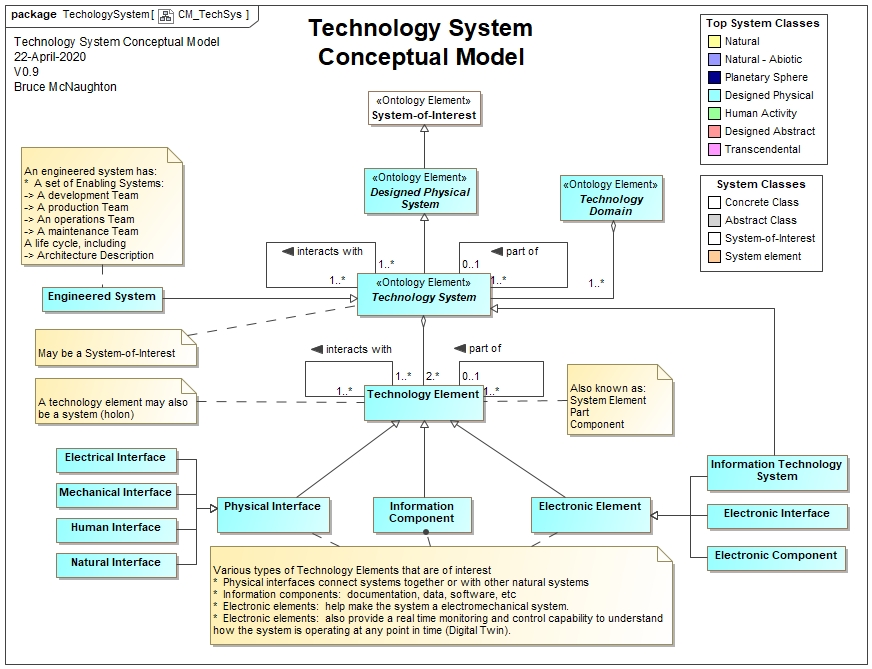
The technology system is a pattern of an IT enabled technology system that may be used in an Internet of Things (IoT). When the Information Technology System is not present, the IoT interface will not be available.
The ability to connect a set of Technology Systems into a System of Systems (SoS) is also possible through the interface to provide a number of interfaces together.
The technology system can also be referred to as an 'engineered system' or 'system-of-interest' in ISO 15288:2015.
The purpose of an Technology System is to provide a pattern that can be used for any technology system that can be interconnected into an IoT. This abstract system can be used as a pattern for any technology (engineered system) developed within an Enterprise.
The Technology systems consist of two types of systems:
- One set of technology is common to all organizations
- Information Technology (foundation element Information System). To be covered in an Information Technology Architecture Description Framework.TBD.
- One set of technology is unique to either production capabilities or product and service delivery.
- Other technology: each system with their own Architecture Description Framework.
- Transportation systems: e.g. Car, Aircraft
- Food Processing
- etc.
The technology systems are considered the 'white box' where the technology needs to be created or tailored in order to support the organization to achieve its purpose or objectives. The change or enabling system provides the means to create or tailor the technology. The relationship between the management system and the technology systems is shown below:
Systemic Measurable Variables
The key measurable variables for technology are included for the specific type of technology system being described. Two examples are provided: Hammer and information technology system.
Systemic Capabilities or Functions
The capabilities of the technology
- These are provided for a specific technology system
System States
An information system has the following states:
- Proposed
- Planned and Designed
- Developed
- Tested
- Operational
- Retired
(to be defined as part of the development of the CAFF for the Information Technology System of Systems (SoS)and in the Information Technology System of Systems (SoS) architecture description framework:
Systemic Quality Properties
Non functional systemic properties
MTBF, Security, Safety, etc.
System Quantity Properties
Weight, Size, etc
Operational Stakeholders
Manager
- is the technology fit for purpose in our team?
- do we have sufficient trained people to use and maintain the technology?
- do we understand the risks of using the technology?
People
- Do I understand the purpose and how to use any technology?
- Do I have the skills, knowledge and experience to carry out the work using the technology?
- Is the information system easy to use?
- Do I value the information system as a means to achieve my objectives?
Enabling System (programme, project, development, production, support)
Manager
- Do we have the business case that justifies the development (costs / benefits)?
- Do we have a plan that is achievable?
- Have we understood all of the elements in the life cycle?
People.
- Do we understand the requirements for the technology?
- Do we have the skills, knowledge and experience to carryout the plan?
- Do we understand how the technology will be used?
- Do we understand the full life cycle elements necessary to produce the technology?
Information Technology Systems form part of the Information Technology Systems needed for the enterprise. This information technology may be a subset of the entire set of technology used within an organization.
Information Technology Systems can be either COTS (Commercial off the shelf - typically black box) or developed within the organization (typically white box). The information technology system in use becomes an asset of the organization.
An information system fits within the full set of information systems used in a Organization. The total set of information systems is identified in the Information Technology Architecture Description. The network viewpoint highlights the number and types of information systems used in an organization.
The environment for the information technology systems is both the full set of technology inside the enterprise and the specific technology used within a Organization. Other factors outside of the enterprise include:
- Rate of technology change
- Requirements and external standards that must be met
- Security and continuity requirements external to the enterprise.
Interfaces and Flows
- What interfaces are involved with material flow?
- What interfaces are involved with energy flow?
- What interfaces are involved with information flow?
- What other interfaces are needed?
An information system is the basic building block in the Information Technology System of Systems (SoS).
System Element: Identification and Relationships
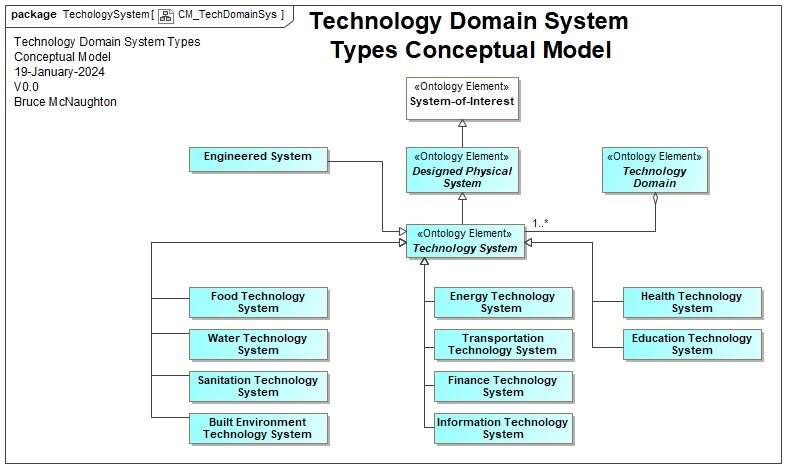
With the following Technology Domain System Types (Initial List):
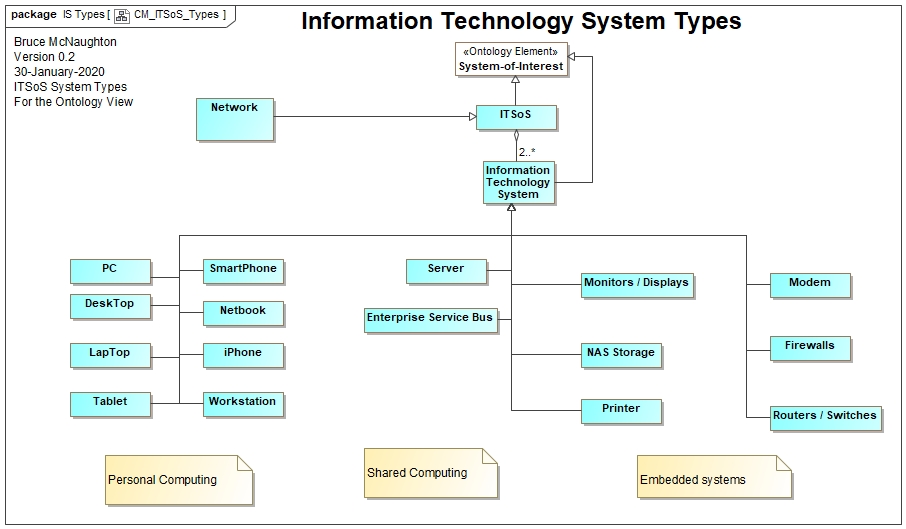
With the following Information Technology System Types:
With the following Information Technology System types for an IoT (initial list):
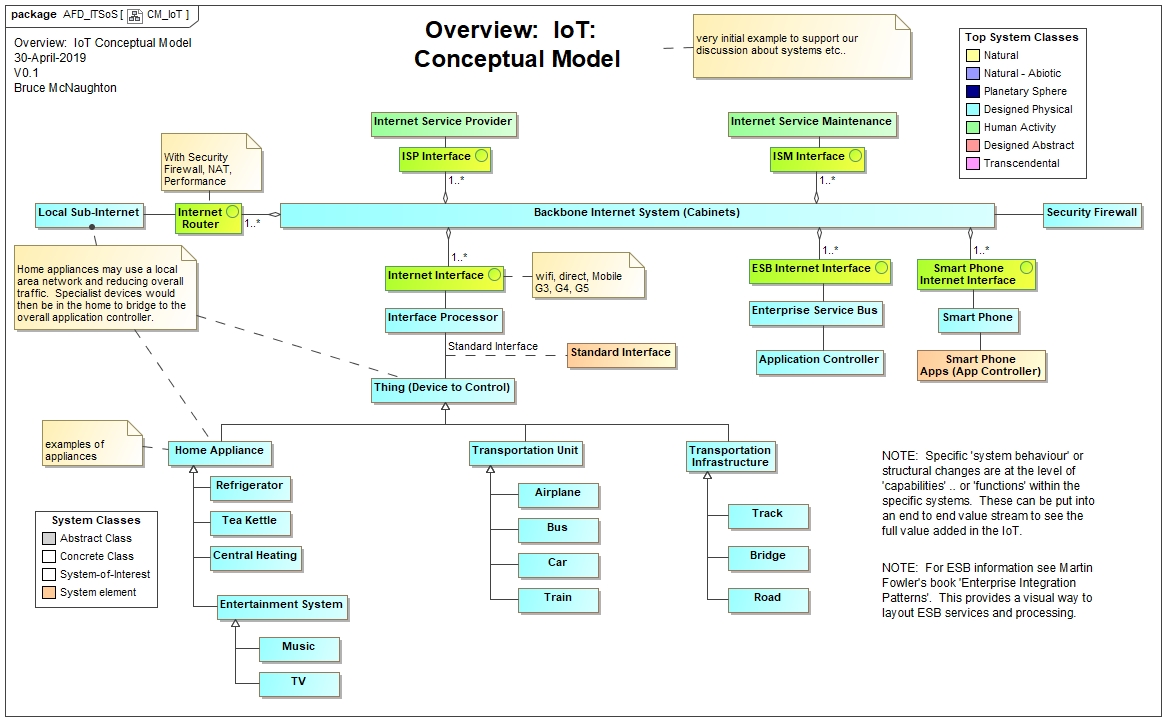
Configuration / Scenario:
Describes any configuration / scenario attributes for a specific system-of-interest. This may not be appropriate for all system descriptions (e.g. patterns or abstract systems).
Cyclical (Repeating / Regular) Processes
Normal Use
Maintenance
Recovery from failure.
Development Life Cycle Processes
Adaptation
New Product Development (replacement of existiing)