Description
The People Viewpoint describes the approach to creating the People View for an Architecture Description.
People are the active elements of a management system. A person
- Is an integral part of the capabilities of the organisation
- Contributes to the organisation through their work
- Uses technology to improve their productivity and reduce errors
- Create and use information to support their decisions and produce results
- Interact with other people across the organization in formal and informal social networks.
- Uses a process to guide their work
People bring or develop the following:
- skills, knowledge, experience, attitudes, behaviours and beliefs
- a wider understanding of the organisation and how it works
- Understanding of how they learn and change
- their physical and mental processing capabilities.
This viewpoint also looks at the capacity and competency of the people allocated to the teams
This viewpoint also identifies the various 'User or Customer personas' that are key to the delivery of products or services. These user personas represent a class of people and identify unique profiles of skills, knowledge, experience, attitudes, behaviours, beliefs and physical attributes. These customer and user personas help ensure that the appropriate user or customer experience is achieved and the expected capabilities (internal and external) are realised.
This people view identifies all of the stake holders types and key roles for the enterprise and the organization.
Rationale
- People are an essential part of the organization. Managers create the environment for people to be successful. People bring their skills, knowledge, experience, attitudes, behaviour and beliefs to their team to contribute to the purpose of the organization.
- Managers are a subset of the people in the organisation and create the environment for their teams success.
Stakeholders and their Concerns
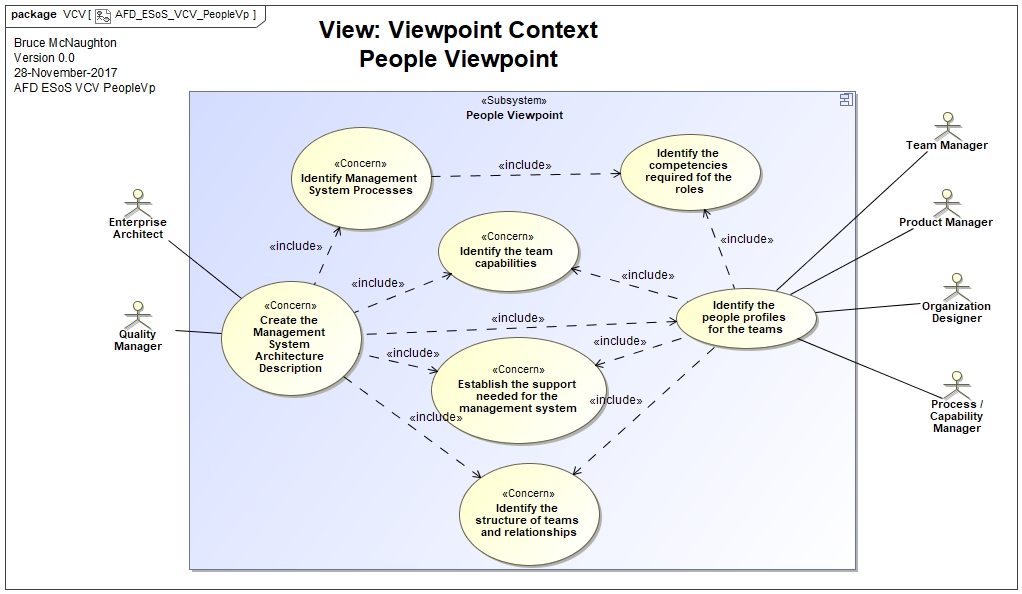
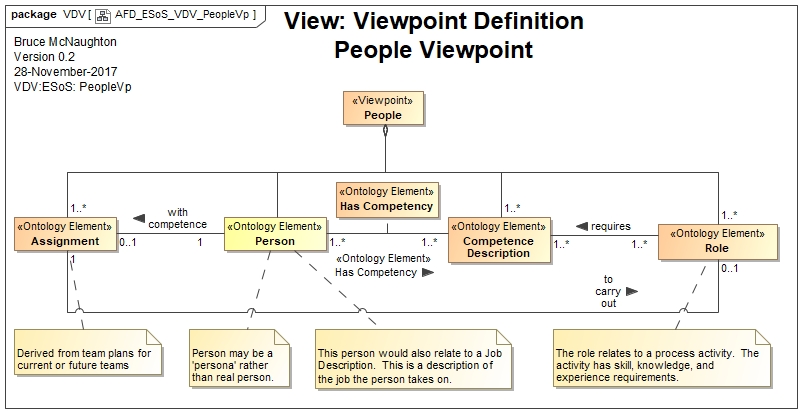
Ontology Concepts and System Descriptions
System Descriptions: Person, Team, Team Capability
Models
Jobs / Role Model, Job / Skill Model, Succession Planning Model, Responsibility Chart (RASCI![]() RASCI represents the various responsibilities that a Person can take when carrying out an Activity and Role.
RASCI means: {Responsible, Accountable, Support, Consult, Inform}.)
RASCI represents the various responsibilities that a Person can take when carrying out an Activity and Role.
RASCI means: {Responsible, Accountable, Support, Consult, Inform}.)
Target People Survey results., Social Network Model, User Persona Model and profiles.
Steps to Create the View
- Identify the critical skills, knowledge and experience needed for the critical capabilities
- Create a job / role model to highlight the key skills, knowledge and experience
- Identify the typical job / role progression within the Job / Role Model.
- Identify the capacity for the selected state in terms of critical job / roles
- Identify the attitudes, behaviour and beliefs necessary to carry out this work
- Create a social network model (formal relationships) using the process descriptions.
- Identify customer or user personas (internal or external) to help ensure that the capabilities will be fit for purpose.
Correspondences
CR01:
Examples
Skills Framework for the Information Age (SFIA)
Sources
- Business without Bosses, Charles C. Manz and Henry P. Sims, JR.
- Cultural Web
- Dance of Change, Peter Senge and Others
- Management and Organisational Behaviour, Laurie J Mullins
- Management: Tasks, Responsibilities and Practices, Peter Drucker
- Organization Design, Jay Galbraith
- Organizational Culture and Leadership, Edgar H. Schein
- The 7 Habits of Highly Effective People, Stephen R. Covey
- The Human Side of Enterprise, Douglas McGregor
Notes
- SFIA like model of the career paths / progression
- Skills Capacity models
- Permanent / Contract / Outsourced Mix
- Responsibility Charts
- Customer and User Personas used in agile development and business process design. These personas help ensure that the customer / user journey is fit for purpose.
This people view also looks at the culture that emerges from the organization and the implications across the various models to enable a culture in line with stated vision and values for the organization. This may relate to the design of measurements and analysis of cultural changes on other aspects of the people or the capabilities.
See Cultural Web.