Work Product Description
A process![]() set of interrelated or interacting activities that use inputs to deliver an intended result. ISO 9000:2015. is a set of interrelated or interacting activities that use inputs to deliver an intended result. ISO 9000:2015.
set of interrelated or interacting activities that use inputs to deliver an intended result. ISO 9000:2015. is a set of interrelated or interacting activities that use inputs to deliver an intended result. ISO 9000:2015.
Interrelated or interacting: The activities within the process work together to produce the intended results required to achieve the objectives and goals of the process.
Activities: descriptions of two or more activities to be carried out by people in the organisation. The activities also identify the Technology Interaction Points.
Inputs: The work products to be used or conditions necessary to carry out the activity
Intended Result: The intended result can be an output of a process, a product or service from the organization. Other terms used are work product, outcome, etc.
A Process Description contains the top level information about a specific process. This process description working view of the whole process and supporting information.
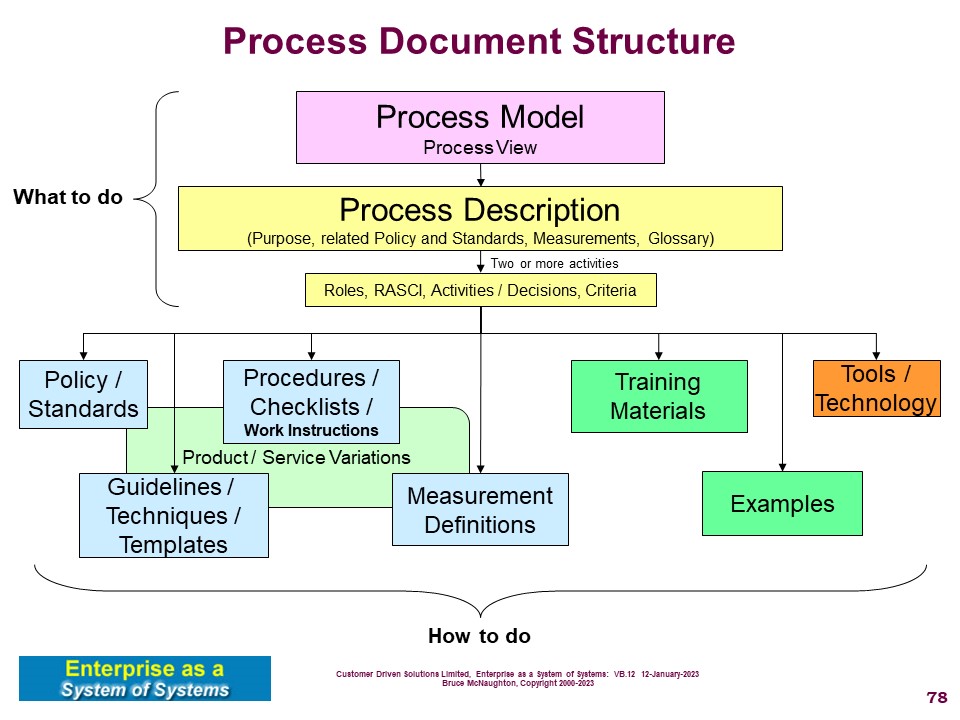
The supporting documentation are all referenced through the process description to keep the process description focused on 'what to do' rather than the details of how to do the work.
Over time, the use of this document will reduce as people become competent using the process. The process description is also the starting point for any improvements to the process.
The process description and the supporting documentation becomes the full body of knowledge about the process.
Contents
The Process Description contents are:
- Introduction
- Purpose / Scope
- Objectives
- Measurements
- Process Activity Model
- Roles and Responsibilities (Process Responsibility Chart)
- For each Activity: Activity Description
- Tools and Training
- Document and Record Retention
Formal Support Documentation
- Policy
 Set management direction and intention A policy is a statement of the management
intention and direction. The
Policy is a short document and is mandatory. Standards
establish the minimum acceptable criteria for the work.
Set management direction and intention A policy is a statement of the management
intention and direction. The
Policy is a short document and is mandatory. Standards
establish the minimum acceptable criteria for the work. - Procedure
 Step by step way to do a critical activity or part of an activity to ensure that the activity is carried out in a repeatable way. Generally mandatory. Procedures are used to ensure that critical
work is performed in a consistent way. A
procedure states how to carry out a work item and is mandatory.
Step by step way to do a critical activity or part of an activity to ensure that the activity is carried out in a repeatable way. Generally mandatory. Procedures are used to ensure that critical
work is performed in a consistent way. A
procedure states how to carry out a work item and is mandatory. - Standard
 Sets the minimum acceptable standard for carrying out all or part of a defined activity. Establishes the minimum criteria for an area.
Sets the minimum acceptable standard for carrying out all or part of a defined activity. Establishes the minimum criteria for an area. - Guideline
 Best practice information on how to carry out an activity. Guidelines and Techniques provide guidance
and best practice information to people carrying out an activity within
the process. These
are generally non mandatory and are generally introduced through training
or examples. Checklists
may also be used to provide support for using the process
Best practice information on how to carry out an activity. Guidelines and Techniques provide guidance
and best practice information to people carrying out an activity within
the process. These
are generally non mandatory and are generally introduced through training
or examples. Checklists
may also be used to provide support for using the process -
The inputs and outputs are also described in this set of documentation. This also includes the definitions of the templates for documents, forms, or other information objects.
- Techniques
 Recommended approach to performing an activity. These may be reused across many activities.
Recommended approach to performing an activity. These may be reused across many activities.
- Checklists
- Template
 A recommended approach to creating a document and capturiing the information in a common format. A starting point for creating a work product.
A recommended approach to creating a document and capturiing the information in a common format. A starting point for creating a work product. - Link to Process Design Patterns PDF A way to reuse existing designs or create new process design patterns. An example is the Capability Innovation Life Cycle. See Process Design Pattern Template
Detailed Support Documentation
- Measurement Specification
- Glossary of Terms
- Training Materials provide a way to transfer knowledge about a process. There is generally a structured set of materials which can be used by an individual (self study) or in a classroom environment. There may be an instructors guide, a workbook, some examples, etc.
- Additional guidance materials to help carry out the process
- Example of how to use the process
- Exercises to help practice the activities within the process.
- Practical and relevant examples are critical to a consistent implementation of a process. These may be created during development as a sample of expected best practice for use in piloting. The pilot teams using the process may then provide examples for the roll-out.
- Tools can provide both productivity and accuracy gains for people implementing the process. These must be carefully specified and evaluated by the team for suitability for use in the organisation.
- Descriptions of associated tools
- Examples of using the tools
- User guides or online help.
Processes Creating, Updating and Using this work product:
Created and Updated: Capability Innovation Life Cycle
Completion Criteria:
Process Description has been reviewed and approved.
Process Owner has taken responsibility for the process.
Examples
The Managing Successful Projects (PRINCE2) Manual is an example Process Description for the Project Management. This PRINCE2 manual can also be condensed to 15 to 20 pages if people are all trained on the process. So given the correct training, the actual Process Description may be very small.